Examples
Phospholipase inhibited by ibuprofen
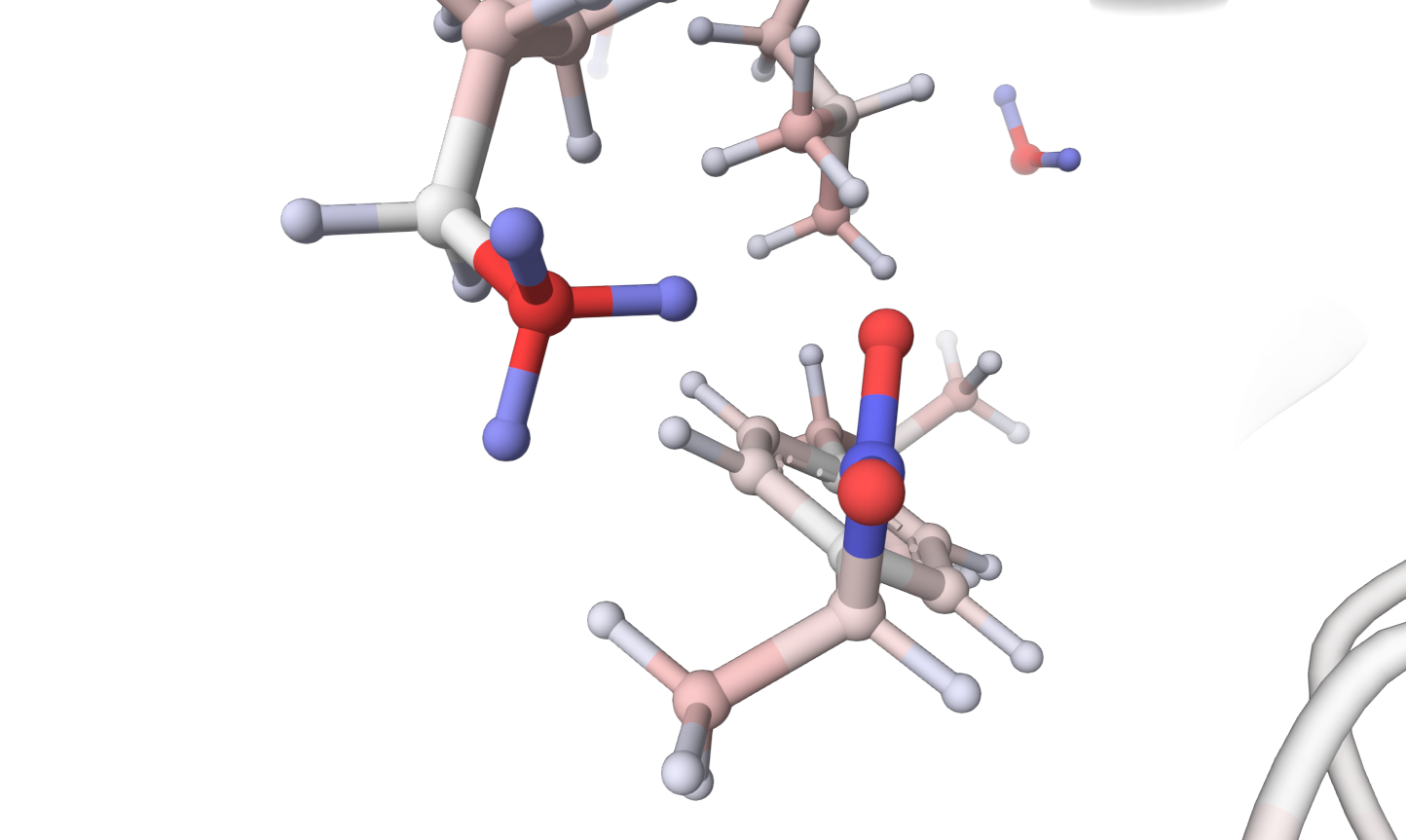
Phospholipase A2 is an enzyme that occurs in plants, mammals, snakes, and bee venoms.
It catalyses the hydrolysis of the ester bond in phospholipids in the cell membranes.
Hydrolysis products are lysophosphatidic acid and free fatty acids, which can disrupt cellular membranes and
induce inflammatory responses (Burke2010). The carboxyl group of ibuprofen interact,
creating an electrostatic bond to lysin (LYS 60) in phospholipase A2 and inhibiting its function.
Based on this knowledge, we can develop therapeutics that can reduce the inflammatory reactions
associated with snakebites (Gaspar2010).
Carbohydrate binding lectin
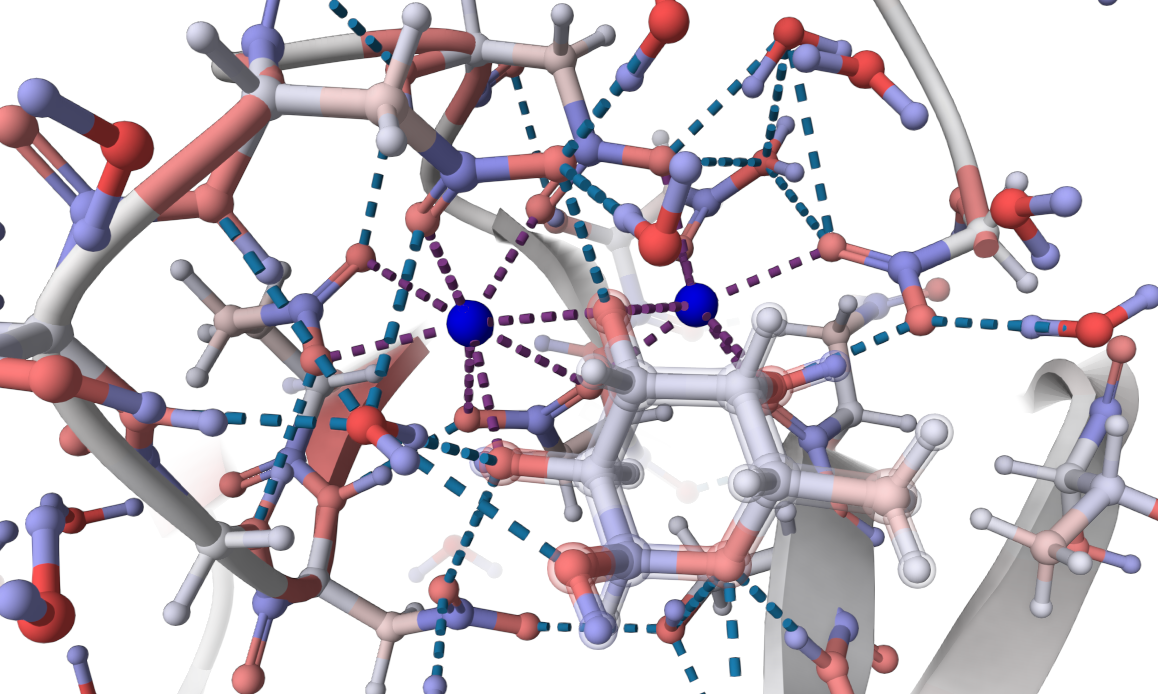
Lectin PA-IIL from the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa plays a key role in its pathogenicity (i.e., it can cause cystic fibrosis, which has high mortality) (Imberty2004).
This lectin has an unusually high affinity for carbohydrates due to its unique binding mode involving two calcium ions
(Mitchell2002). The calcium ions form ionic bonds with residues
in the protein and with three hydroxyl groups of the fucose molecule (chain C: FUC 1118).
This interaction results in a stable complex through
extensive charge delocalisation. Unlike most protein-carbohydrate interactions, PA-IIL relies on ionic
and coordination bonds with minimal hydrophobic bonds, presenting the structural role of calcium ions
in stabilising the binding site (Mitchell2005, Adam2007).
Potassium channel
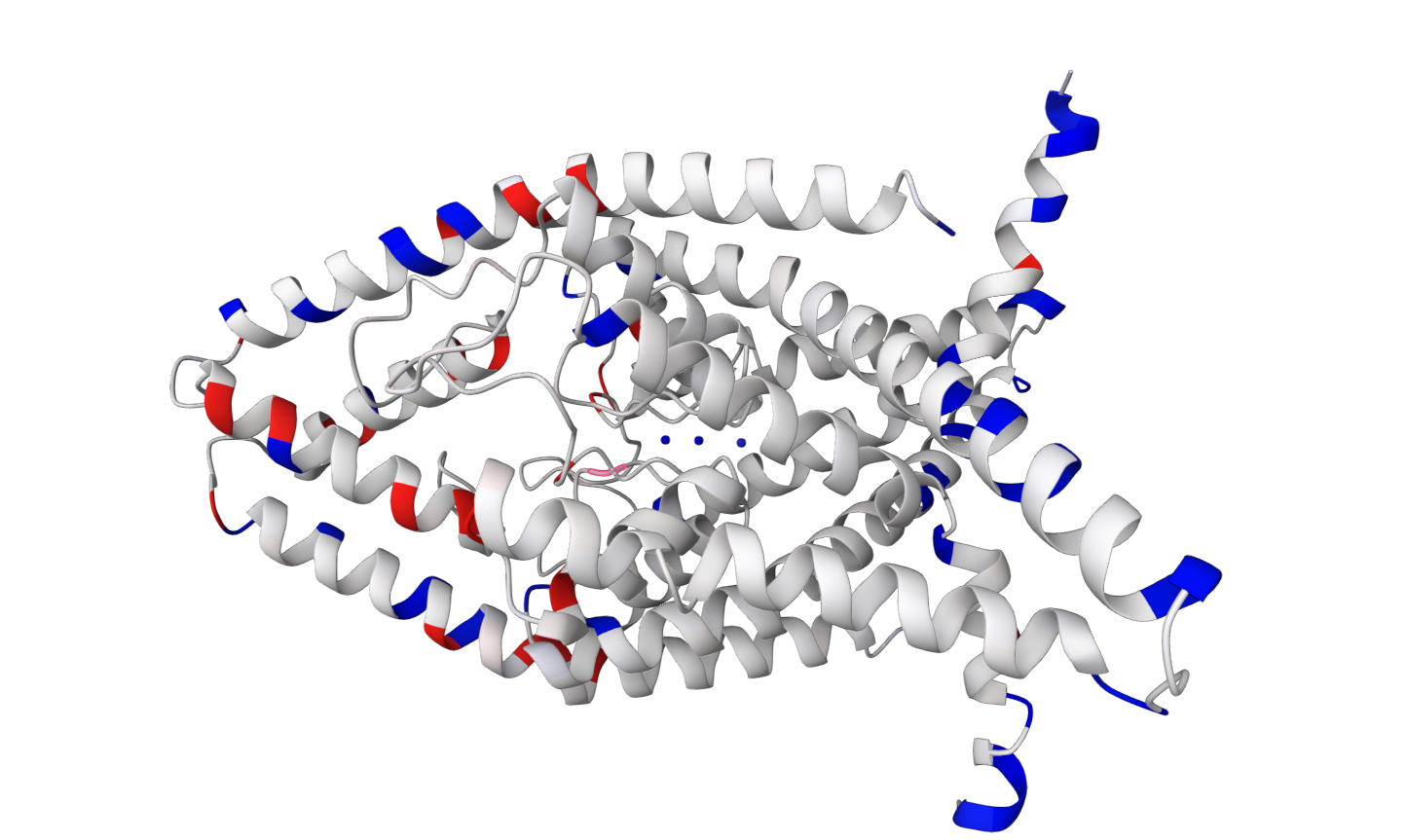
TASK2 (TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel 2) is a pH-gated ion channel belonging to the two-pore domain K+ (K2P)
channel family (Reyes1998).
This channel maintains cellular homeostasis and regulates physiological
responses to environmental changes. The transmembrane regions of TASK2
are characterised by their nonpolar nature and lack of charge, distinguishing
them from the intracellular and extracellular domains of the protein (Li2020).
If you found
PDBCharges helpful,
please cite:
Schindler, O., Svoboda, T., Rošinec, A., Raček, T., Bučeková, G., Tichý, D., Berka, K., & Svobodová, R. (2025).
PDBCharges: Quantum-Mechanical Partial Atomic Charges for PDB Structures.
Nucleic Acids Research.
Are you interested in a research collaboration? Feel free to
contact us.

PDBCharges tool is
a
part
of services provided by
ELIXIR
–
European research infrastructure for biological information.
For other services provided by ELIXIR's Czech Republic Node visit www.elixir-czech.cz/services.
For other services provided by ELIXIR's Czech Republic Node visit www.elixir-czech.cz/services.
Licence conditions in accordance with § 11 of Act No. 130/2002 Coll. The owner of the software is Masaryk
University, a public university, ID: 00216224. Masaryk University allows other companies and individuals to
use this software free of charge and without territorial restrictions in usual way, that does not depreciate
its value. This permission is granted for the duration of property rights. This software is not subject to
special information treatment according to Act No. 412/2005 Coll., as amended. In case that a person who
will use the software under this licence offer violates the licence terms, the permission to use the
software terminates.